 Learn Metallurgy
Learn Metallurgymail@learnmetallurgy.com
Molecules or solids are formed when atoms come together and bond with each other. The nature of the bond depends on the type of atoms involved in bonding.
The Potential Energy relative to atomic distance is given by :-
\[ U(r) = 4\epsilon \Big[ \Big( {\frac{\sigma}{r}}^{12} - {\frac{\sigma}{r}}^6 \Big) \Big] \]
On differentiating U repect to 'r' gives force(F):
\[ F = -\frac{dU}{dr} \]
And, again on differentiating F repect to 'r' gives Stiffness:
\[ S = \frac{dF}{dr} = \frac{d^2U}{d^2r}\]
Notes :
(1) Curvature ∝ E (Elastic Modulus) [ As \( E = \frac{S}{r_{0}} \)]
(2) For Shallow curve( U ), E is less
(3) For deep curve( V ),E is high
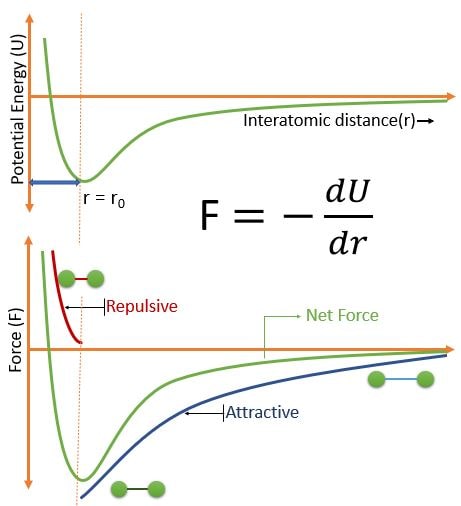
The Above Figure shows that :
• Negligible forces for large interatomic separation
• As atoms come closer to each other, competing forces: attractive and repulsive forces, both of which depend on distance and details of the structure
• Attractive forces: ionic, covalent, metallic, van der Waals
• Repulsive forces: interaction among electron clouds (important at small distances)
• No net forces at distance r0 (approx. 0.3 nm for many atoms).
An ionic bonding is an electrostatic or Coulombic force between an positive ion and an negative ion when they are brought into close proximity
➧ Ionic bonds are also known as 'Elecrovalent Bonds'.
➧ Ionic bond form between a Low ionization energy Positively charge ion( Metal ) and High electon affinity Negatively charged ion (Non-metal) and can not be form between two same atoms.
➧ Ionic bonding is form by transfer of valence electon(s).
➧ Higher the lattice energy, greater the tendency of ionic compound formation.

Properties of Ionic Solids :
(1) Unidirectional or Non-directional
(2) Crystalline in Nature
(3) Hard and brittle
(4) High melting point and boiling point
(5) Good Insulators electicity in solid state but good conductor of electricity in their molten state
(6) Soluable in polar solvents and insolubles in non-polar solvents
(7) Bond energies ranges from 500-1200 kJ/mol
Examples : NaCl , NaF , CaO.
A covalent bond is formed, when two or more electons of an atom, in its outermost energy level and form bond by shearing of electon(s)
➧ In this bonding stable arrangement is achieved by sharing of electon rather than transfer of electon.
➧ Covalent bond is formed between two non-metals, and can be formed between two same atoms.
➧ High ionization energy and High electon affinity of two combining atoms is required.
➧ Covalent bond form when there is Low difference of electonegativity (~0) between two atoms.
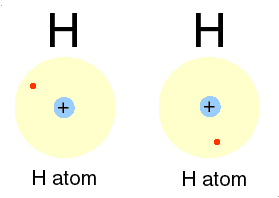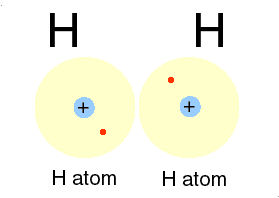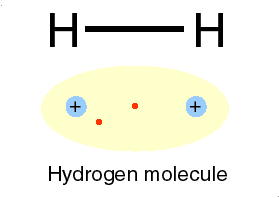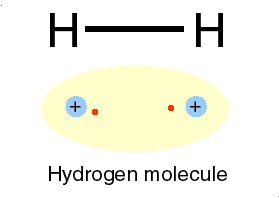
Properties of Covalent Solids :
(1) Directional
(2) Hard and brittle but less than Ionic solids
(3) Low melting point and boiling point. Usually liquid/gaseous state at room temperature
(4) Insulators of heat & electicity
(5) Soluable in organic solvents and insolubles in water
(6) Bond energies ranges from 150-700 kJ/
Examples : H2 HCl, SO2, CO2, and CH4.
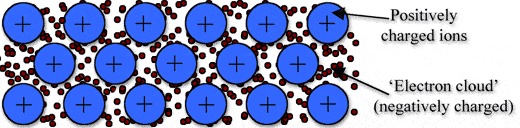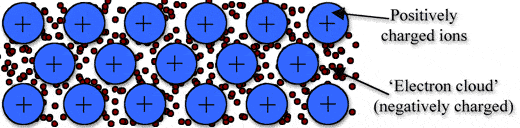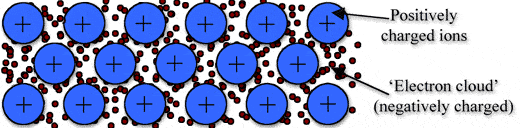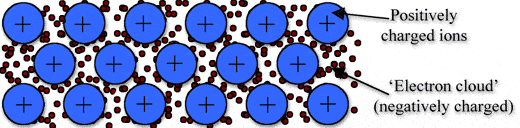
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding, and it is formed by electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons(formed by sea of electrons) and positively charged metal ions.
➧ Metallic bond formed between two metals. But it is the not only type of bond that is formed between metals.
➧ Metallic bonding enhance metal properties like strength,opacity, and luster, ductility, thermal and electrical resistivity and conductivity.
➧ Metallic Bond can be formed only between two same atoms.
 -Image source textbooks.elsevier.com
-Image source textbooks.elsevier.com
Properties of Metallic Solids :
(1) High elastic modulus
(2) High strength
(3) Good electrical conductivity
(4) Good ductility
(5) High Reflectivity
(6) Bond energies ranges from 50-850 kJ/
Examples : Na, Mg, Al.
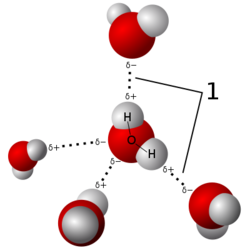
Hydrogen Bond formed due to forces produced by atomic or molecular dipoles.Actually the Covalent bonded atoms often produce an electric diapole configuration with hydrogen atom as the positive end of diapole.
➧ Dipoles formed due to high electronegative element like nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F).
➧ It is an secondary bond, which is much weaker than primary bonds.
➧ They are found in most materials, but their effects are often neglected due to the strength of other primary bonds.
Properties of Hydrogen Bonded Solids :
(1) Directional
(2) Relatively strong bond than other secondary bonds
(3) Low Melting point
(4) No valence electon means good insulators
(5) Soluble in both polar and non- polar solvents
(6) They are transparent to light
(6) Bond energies ranges from 10-150 kJ/
Example : water , CHCl3 , NH3
Weak and temporary bond between atoms or molecules. And it is an distance-dependent interaction and vanishes at larger distances between the interacting molecules
➧ Have Lower melting points
➧ Softer than ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.