 Learn Metallurgy
Learn Metallurgymail@learnmetallurgy.com
As we have learn earlier the max packing faction is 74% (in HCP Or FCC) and the remaining space is void. Voids in solids is the vacant space between the constituent particles in a closed packed structure.
The size and distribution of voids in solid have a considerable effect on behaviour of materials property. eg, More is the void more will be diffusivity, and also affect the interstitial solubility.
Types of Voids :
(1) Tetrahedral
(2) Octahedral
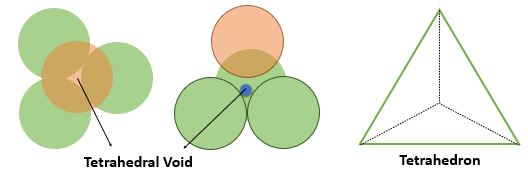
Tetrahedral Void :
The tetrahedral Void form in crystal structure when the sphere of top layer lie just above the triangular voids formed be layer lying just below. A tetrahedron is formed by joining radius of all four spheres and the vacant space between them is tetrahedral void.
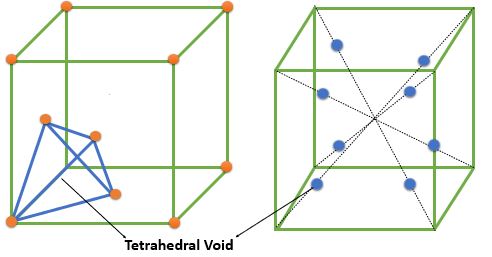
➧ The FCC crystal structure have 8 tetrahedral voids which are located near the corners of cell. All Tetrahedral voids lie inside the cell
➧ The number of tetrahedral voids is 2 times the number of the atoms in cell.
➧ The size of largest interstitial atom that can fit into tetrahedral Void = \( 0.225 \times \textrm{ Size of FCC atoms} \)
\[ \textrm{n atoms} \Rightarrow 2 \times \textrm{n Tetrahedral Void} \]
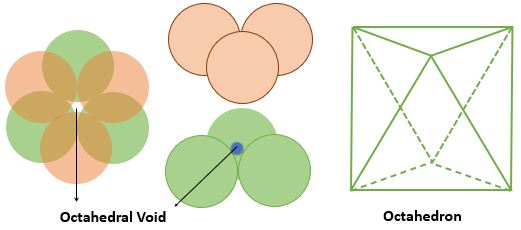
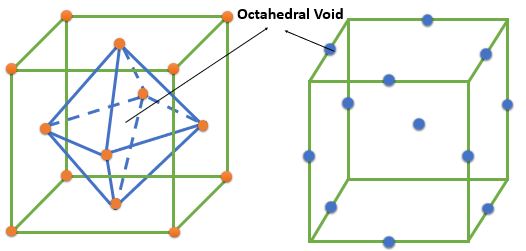
➧ The FCC crystal structure have 4 octahedral voids which are located at the :
1) Center of cell = 1
2) At every edge center contributing 1/4th => \( \frac{1}{4} \times 12 = 3 \) Voids
➧ The number of octahedral voids is equal to the number of the atoms in cell.
➧ The size of largest interstitial atom that can fit into octahedral Void = \( 0.414 \times \textrm{ Size of FCC atoms} \)
\[ \textrm{n atoms} \Rightarrow \textrm{n Octahedral Void} \]
| Crystal | Void | Position | \( \frac{voids}{unit} \) | \( \frac{voids}{atoms} \) | \( \frac{r_{voids}}{r_{atoms}} \) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCC | Tetrahedral | 8 \( ( \frac{1}{4}, \frac{1}{4}, \frac{1}{4} ) \) | 8 | 2 | 0.225 |
| Octahedral | Body Center : 1 \( ( \frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{2} ) \) Edge Center : 3 \( ( \frac{1}{2}, 0, 0 ) \) |
4 | 1 | 0.414 | |
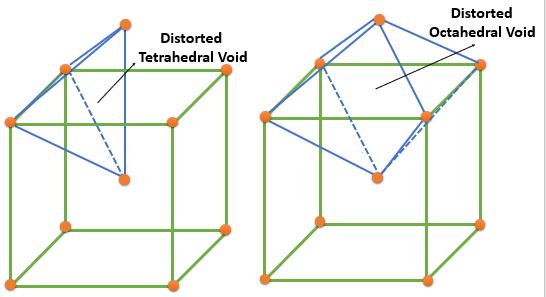
| BCC | Distorted Tetrahedral | \( \frac{4}{2} \times 6 = 12 ( 0, \frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{4} ) \) | 12 | 6 | 0.155 |
| Distorted Octahedral | Face Center : \( \frac{1}{2} \times 6 = 3 ( \frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{2}, 0 ) \) Edge Center : \( \frac{1}{4} \times 12 = 3 \( ( \frac{1}{2}, 0, 0 ) \) |
6 | 3 | 0.291 | |
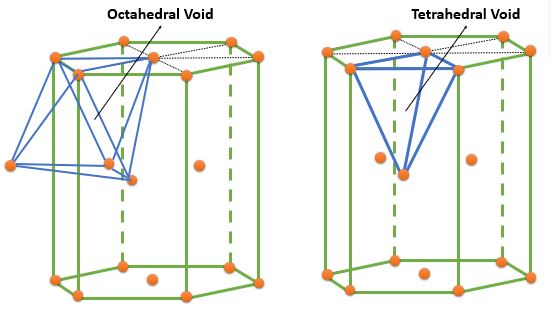
| HCP | Tetrahedral | \( ( 0, 0, \frac{3}{8} ) , ( 0, 0, \frac{5}{8} ) \) \( ( \frac{2}{3}, \frac{1}{3}, \frac{1}{8} ) , ( \frac{2}{3}, \frac{1}{3}, \frac{7}{8} ) \) |
4 | 2 | - |
| Octahedral | \( ( \frac{1}{3}, \frac{2}{3}, \frac{1}{4} ), ( \frac{1}{3}, \frac{2}{3}, \frac{3}{4} ) \) | 2 | 1 | - |