 Learn Metallurgy
Learn Metallurgymail@learnmetallurgy.com
Thermodynamics is the branch of science that involve relations between heat, work and other forms of energy and their effect on the system and surroundings.
System : A system can be defined as a quantity of matter (or substance) or region in space where our study is focused.
Surrounding: The mass of region outside the defined system is known as surrounding. The Boundary between system and surrounding can be physical or imaginary, rigid or movable.
The part of the surrounding which is affected by the system is called as immediate surrounding.
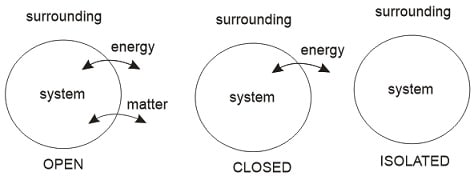
| System | Mass | Energy | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open System | Yes | Yes | Tea in a Cup |
| Closed System | Yes | No | Tea in a cup with top covered |
| Isolated System | No | No | Tea in a thermo-flask |
Any condition of characteristic of the system which defines system specifications like Pressure,Temperature, Volume and etc. And minimum number of such independent veriable defines the Degree of freedom.
INtensive or INtrinsic : A system which is INdependent of mass or mole.
Examples: Temperature , Pressure Density etc.
Note : All Specific properties Intensive properties like Specific Volume, Specific Internal Energy, Specific Entropy, Specific Enthalpy.
Extensive or Extrinsic : A system which is dependent on mass or mole of the system.
Examples: Total enthalpy, Total Volume, Total Energy, Entropy.
State Function : A point function or state function is a property whose value does not depend on the path taken to reach that specific value (i.e., Independent of past history).
State Functions are exact differential (dU, dV, dT).
$$\int_{1}^2 dU = U_2 - U_1$$
Path Function : In contrast, functions that rely on the path from two values are call path functions. They are inexact differential (𝛿W , 𝛿Q).
The infinite state through which a system passes while moving from an initial state to final state is called as process path and the change in the state is called as process. The proccess can be classified as :
Quasi-static or Quasi-equilibrium process : In thermodynamics, a quasi-static process, is a thermodynamic process that takes place infinitely slow such that the system remain in internal equilibrium. This procress is represented be a joint line on property diagram.
The processses which are not a quasi-static, represented by dash(-) line on property diagram.
Reversible and Irreversible process : A process is said to be a reversible process if it follows the same path as that of the forword path, when reversed in direction and doesn't leave any effect on system as well as on surrounding. Reversible processes are an example of quasi-static process.
When the state variables do not change with time and space is called thermodynamic equilibrium.It is of three types:
(1) Thermal equilibrium : Uniformity of temperature at any point with respect to time.
(2) Mechanical equilibrium : Pressure at any point of the syatem should not change with the but pressure may be different at different points.
(3) Chemical equilibrium : The chemical composition should not change with time.
Homogeneous System : Composition is uniform throughout the system (Ex. salt water)
Heterogeneous System : System in which the composition is not uniform throughout the system (Ex. water and vapour mixture)
Pure Substance : If a substance is of homogeneous chemical composition through out the system.(Ex. Gaseous air)
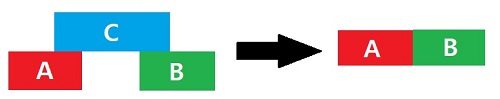
The Zeroth law of thermodynamics states that when a body 'A' is in thermal equilibrium with body 'C' and another body 'B' is also is in equilibrium with body 'C' then body 'A' and body 'B' will also be in thermal equlibrium. The concept of temperature measurement is based on this law.